Research and Devlopment
Go-tech Project
Our duty as sculptors is to express and realize the shape our customers desire under the conditions they require.
To put this into practice, we must not be limited to traditional materials and manufacturing methods, but must continue to study and refine our skills to adapt to a world that is constantly evolving and changing, using new materials and new manufacturing methods.
In order to set the next standard in our manufacturing methods and to be able to meet the uncharted demands of all our customers, we believe it is necessary to constantly take on new challenges.
Here we would like to introduce some of the challenges we are taking on.
National Project Research and Development2023~2025(Reiwa5~Reiwa7)
Note: This contents include Japanese.
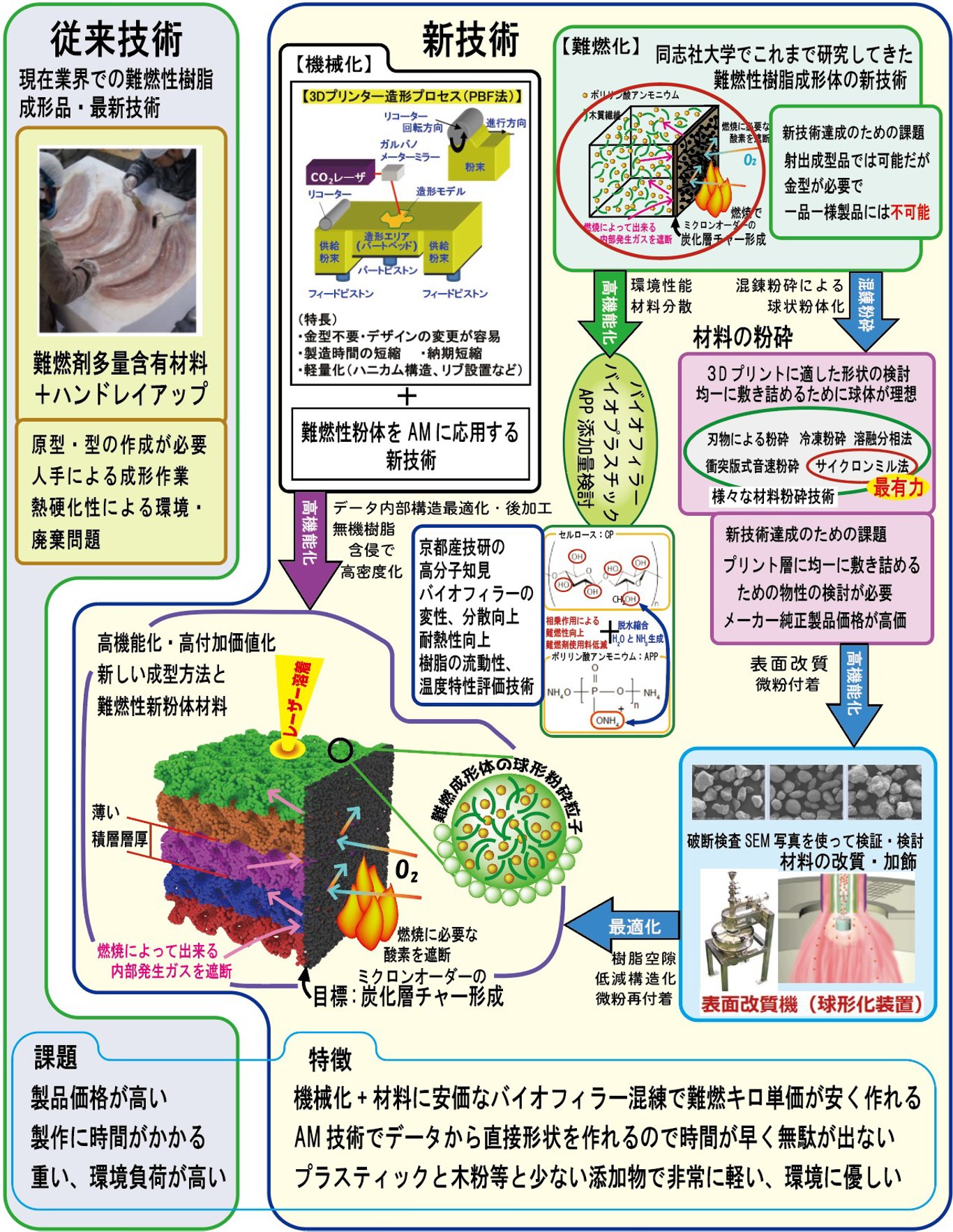
- Development of 3D printer molding powder materials that realize environmentally friendly, flame-retardant, lightweight, and low-cost wall decorative building materials
- Research and development support program for growth-oriented small and medium-sized enterprises
Go-Tech business (former: Support Industry (Sapoin)) -
- Objective
- In the powder bed fusion method, which is currently the most productive additive manufacturing method, flame retardant properties are achieved by using 3D printing materials such as polypropylene, polyamide 11, and polylactic acid resin mixed and ground with flame retardants and wood additives.
Conduct research and development into the materials and manufacturing methods for these objects, and accelerate the BtoC sales process for highly designed, lightweight three-dimensional objects and their materials. - Specific research and development content
-
-
-
- Publication of a paper on the contents of this research and development
- 4DFF 2025 10.23~24
-
- Research on SLS 3D-print molding for fire retardant decorative building materials
Mazuka Kimura①, Hiroaki Ito②, Takeshi Semba②, Yuzo Okudaira③, Tatsuya Tanaka③
①FES Inc., ②Kyoto Municipal Institute of Industrial Technology and Culture, ③Doshisha University
-
- Abstract
- This research concerns 3D printed molding with enhanced fire retardancy by utilizing the carbonization of cellulose. The molding method used is SLS (Selective Laser Sintering Method), which melts and recrystallizes resin powder using laser irradiation; PP (polypropylene) was used as the resin. A 3D printed molded samples containing over 30% cellulose in weight ratio achieved V-0 in the UL94 combustion test, and the mixing rate of the conventional flame retardant was significantly reduced to 1/3 of the previous level. It is expected to be used in public facilities where fire retardancy is required.
- Research on SLS 3D-print molding for fire retardant decorative building materials
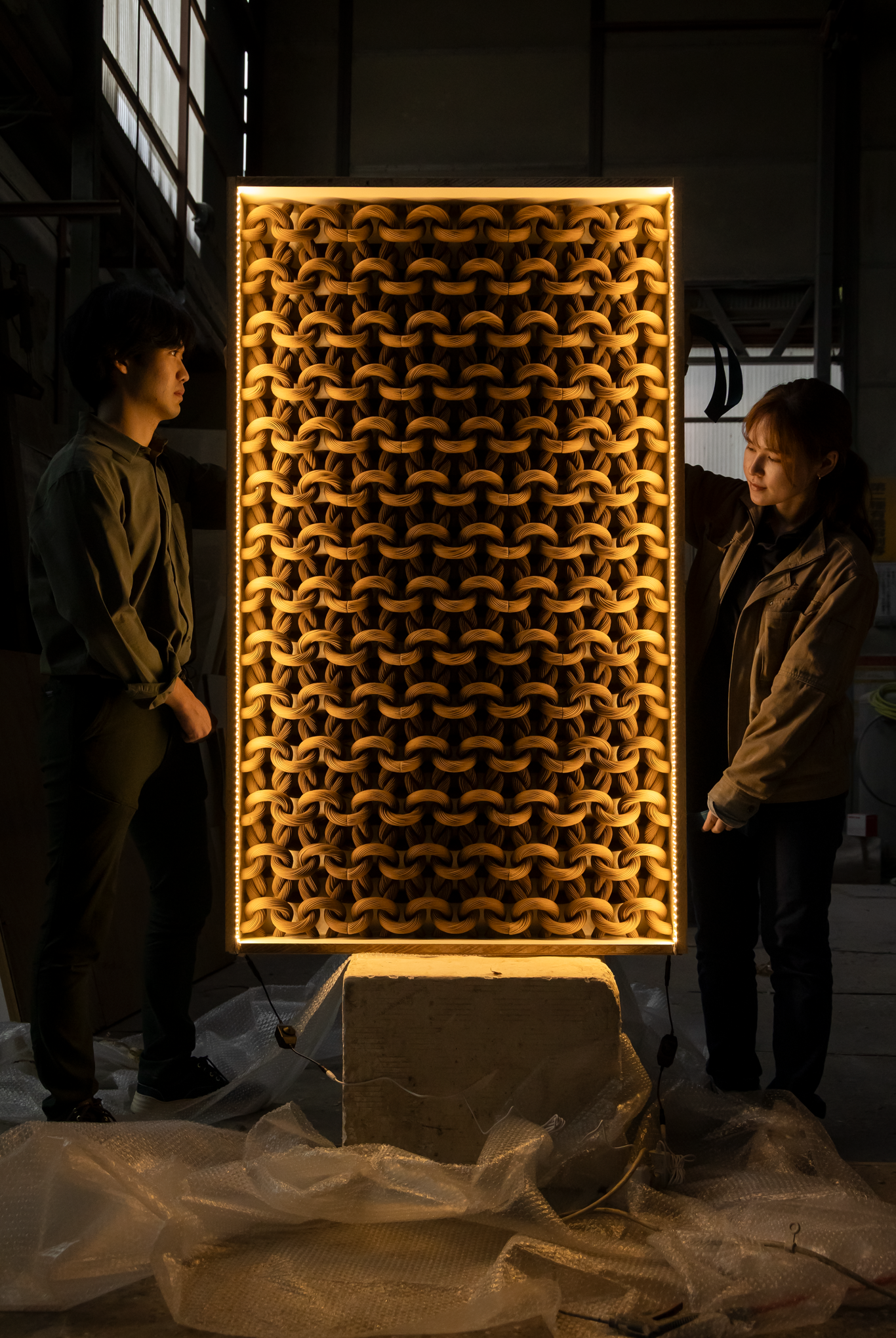

The wall model exhibited at FormNext 2025 is both a work of art and a product sample with commercial applications in mind. Aimed at non-load-bearing wall surfaces where design is the primary focus, such as the entrances and ceiling decorations of luxury hotels and the interiors of shops, we pursued a shape unique to additive manufacturing that removes the constraints of conventional molding methods.
This work is the result of the practice of FES Inc. representative Mazuka Kimura, who has continued his artistic activities since graduating from university, and his ongoing involvement in the creation of works by contemporary sculptor.
This product, which incorporates precision modeling using selective laser sintering (SLS), is positioned as a “touchstone” that will mark an important step in the transition from the display and three-dimensional modeling industries, which have previously relied primarily on thermosetting resins (FRP), to thermoplastic resins, and toward environmentally friendly manufacturing.
The most notable feature of the material design is that the main component is cellulose, and its content exceeds that of the second component, polypropylene. This formulation, which is primarily composed of bio-derived ingredients, has the potential to be an effective solution in an era where carbon neutrality is required. Furthermore, this material has a flame retardancy rating of V-0 according to the UL94 standard, making it particularly noteworthy in terms of safety as a decorative material. In terms of cost, a major advantage is that it uses relatively inexpensive cellulose as its main component while minimizing the amount of flame retardant used.
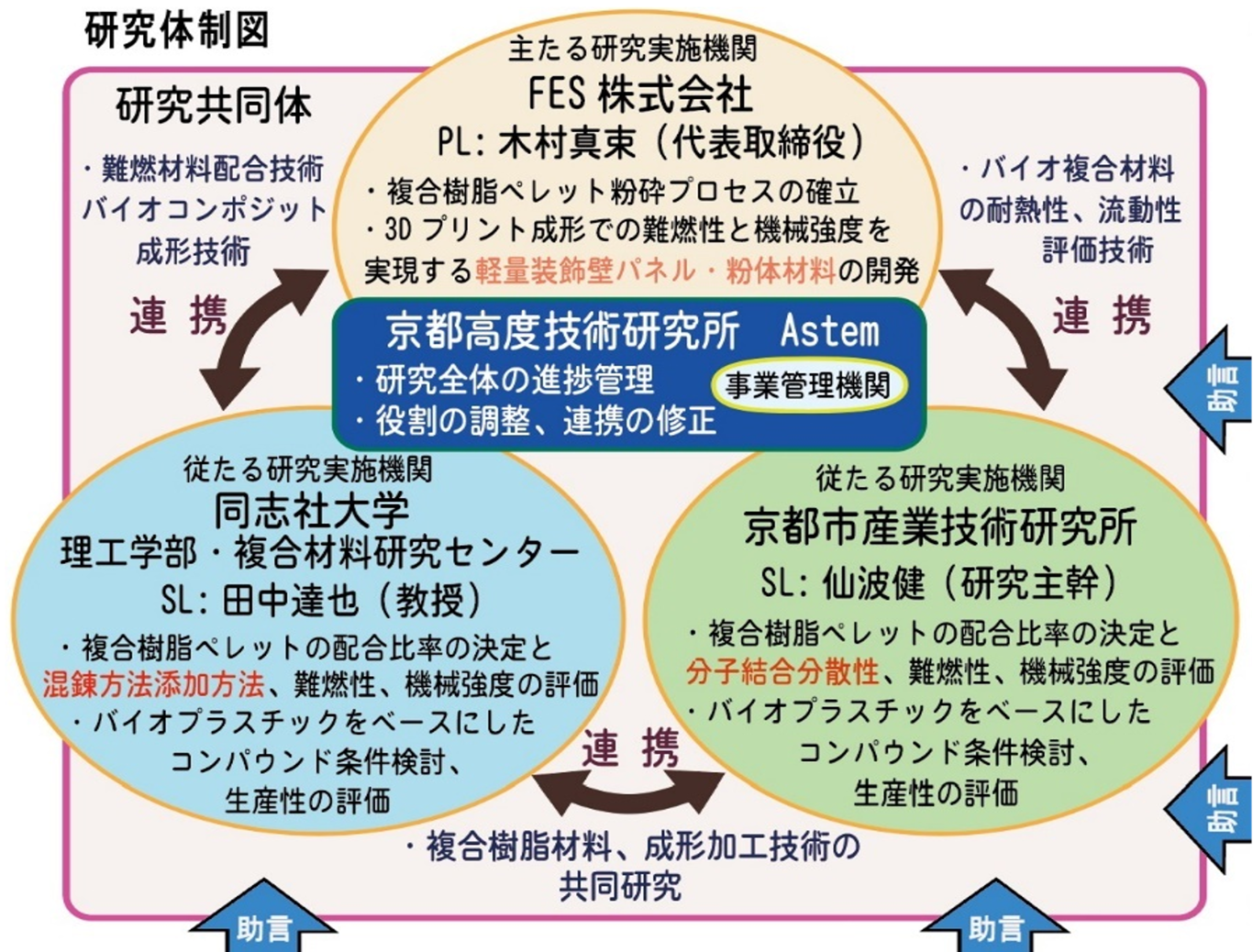
This research is being carried out by FES inc. as a joint industry-academia project with Doshisha University and the Kyoto Municipal Industrial Technology Research Institute. Mazuka Kimura, representative of FES Inc., is a founding member of the artist group “Kyupikyupi,” and currently serves as a bridge to the industry side, using the knowledge he has gained in the field of three-dimensional object manufacturing. Additionally, as the chairman of the Kansai Art and Design Association, he is working to form a cross-industry network and promote new materials and new construction methods.
Acknowledgments
This research was carried out with the support of the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry’s Research and Development Support Project for Growth-Oriented Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises, JPJ005698 (FY2023-FY2025).
We would like to express our gratitude to all those involved.
